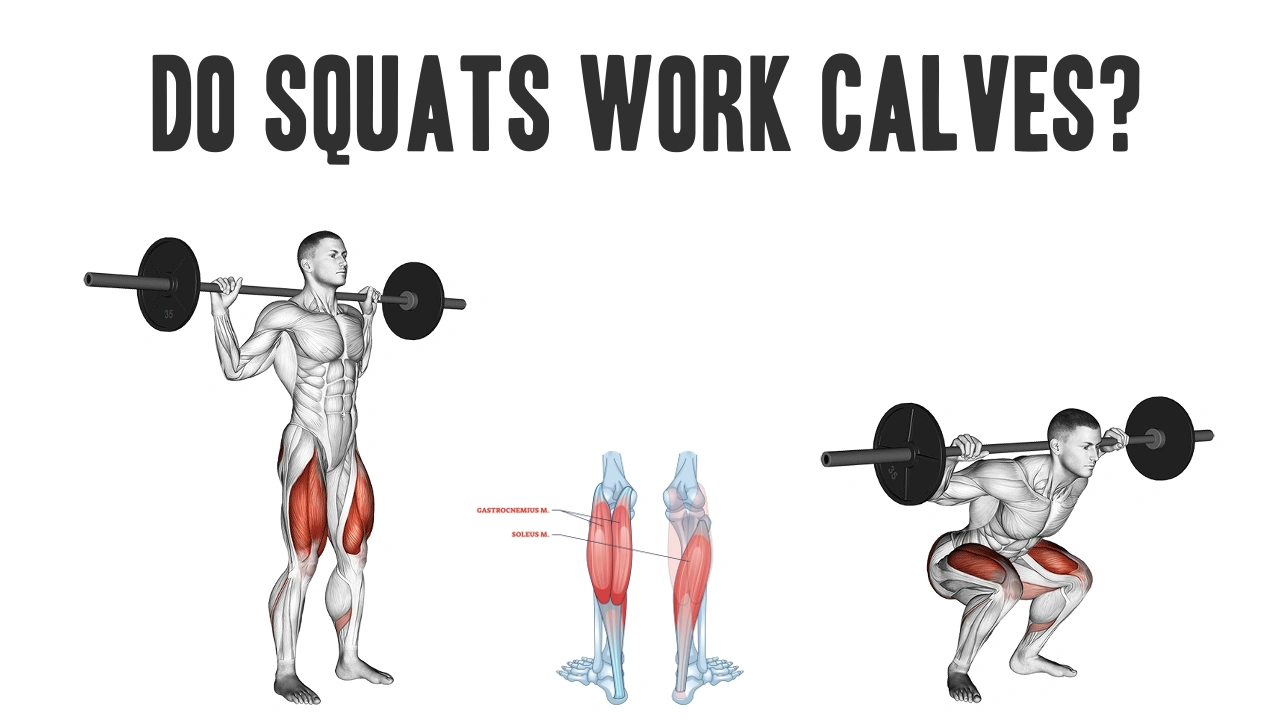
Often as the king of the lower body exercise, the basic muscle is accepted as the square, yeastand shining. What about calves? Ignores the role of many people Calf muscles during the squeezing. Squats actually teach them?
In this article, we will consider anatomical function of the squeezes that are active with muscles and will make you better invest in your training calf.
Calf muscles: brief overall view
It calf complex consists of two main muscles:
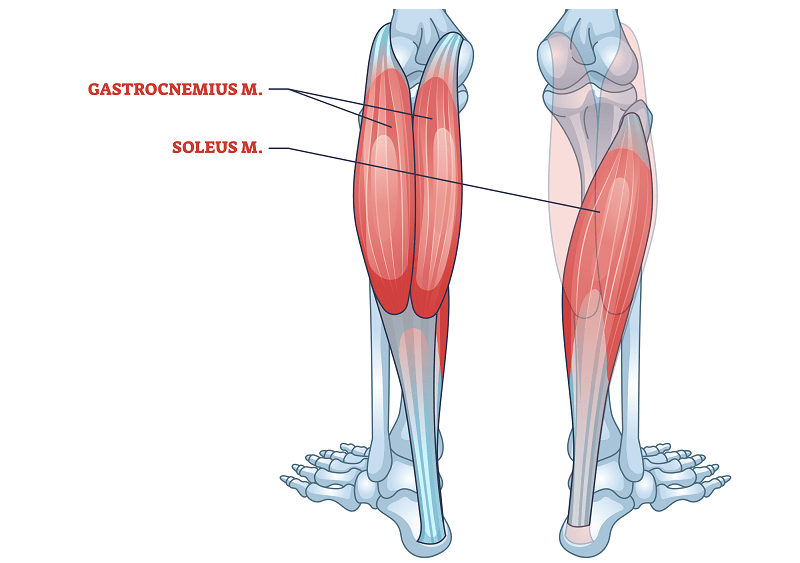
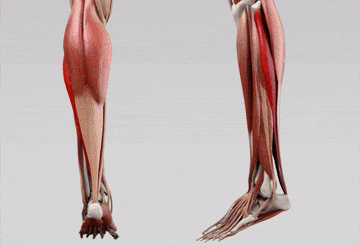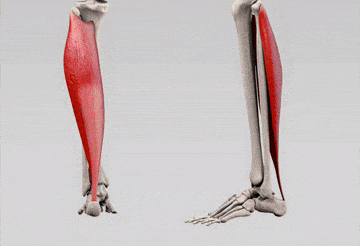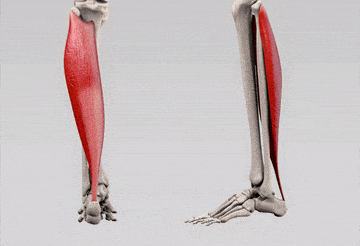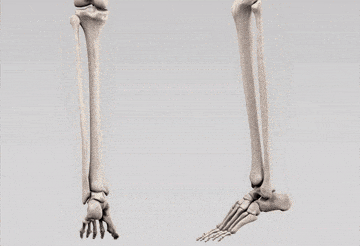
- Gastroxedius – The muscles of a large, visible calf muscle that includes knees and intramuses.
- Individually – Deep muscle under the gastrochnix only that pass the thickness of the ankles.
Together, to manage these muscles visibility (Downturn the leg) and ensure the stability of ankle during stopping and intense.
Saks work calves?
Short Reply: Yes, but indirectly and isometrically.
Why to this:
During the squat:
- It a member of an ankle remains relatively stable (especially in standard backgrowing).
- It individually it Isometric active Help stabilize the ankle and maintain balance.
- It gastroxediuscrosses both ankles and knees Limited activation Because the knees are bent in the movement.
Providing evidence:
EMG studies Calf muscles Intended low level of level During Squats, it is not mainly stabilizing the body and driving the movement.
Key: Cathererantsan and others. (2002) showed that quarters, simulations and vibrations are activated in loud voice on the back low-levelworks first stabilizernot inactive.
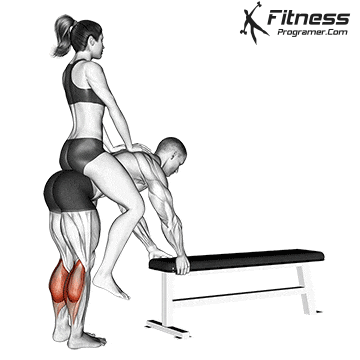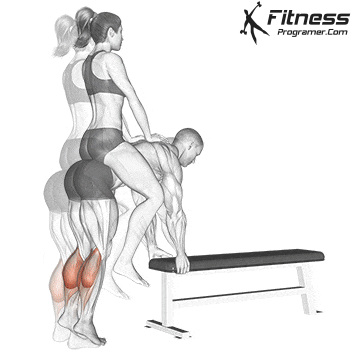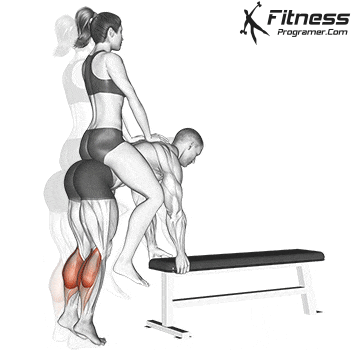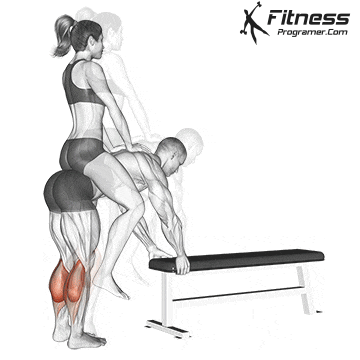
Calf muscle function during Squat: In Fazil
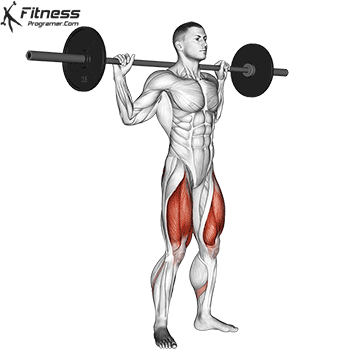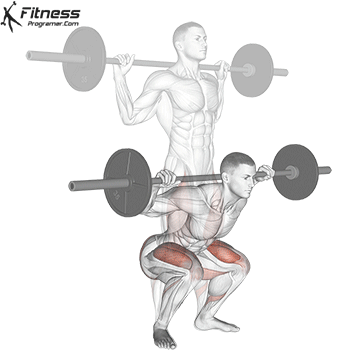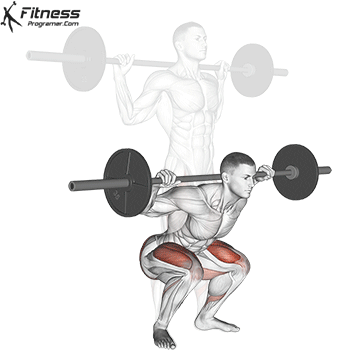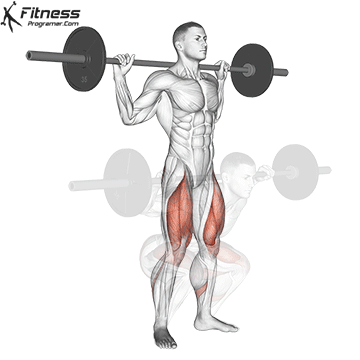
1. Normon (eccentric phase):
- The body bends the hip and knees and ankles.
- It singular agreements in solitary transactions Ensuring and preventing the disorders.
- It gastroxedius Is mainly active because of the lineably flerbergia.
2. Lower status:
- Ankle dormative peaks.
- It Solus remains active Celtic to tibe.
- If a heavy stone shoe (loudly rose), the mobility of the ankle changes the calf.
3. Rise (concentric stage):
- The hips and knees stand up.
- Solus remains activeResist the rage of the hind foot.
- Minimum Dynamic Contribution because it is variable with an extension of Gastotnomia on the top.
How to enhance the calf in Squats
If you want to attract calf muscles at the time of low body, consider the following methods:
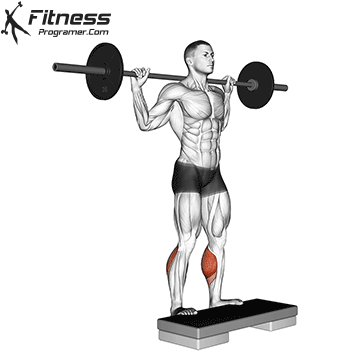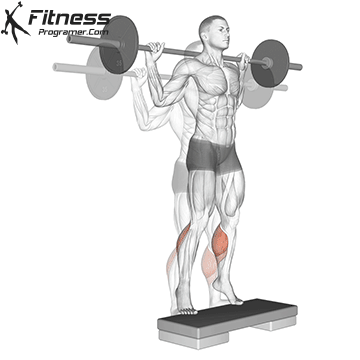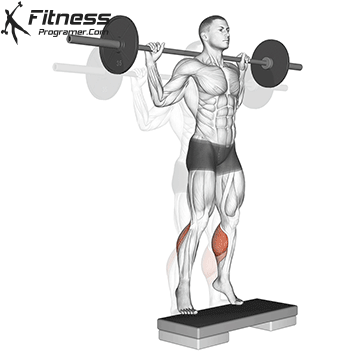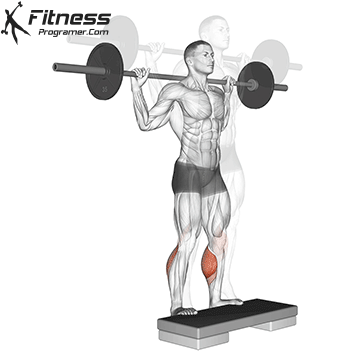
1. Squares with the height of an ankle
- The lifting machine lifting machine increases the demand of planmerformer.
- As this dorsex is increasing, it can increase selus activity a little longer.
2. Add a calf above
- Combine with Calf rises combine the concentric screenfrone.
- Widespread in a widespread training in functional fitness or hypertrophy.
3. Use Tempo squares
- Slowly eccentric and isometric pausees increase stability requirements, promoting the extension of the calf for a long time.
4. Try previous changes
- Gobobet or front circuots move your shooting center, requiring your shooting center and calf.
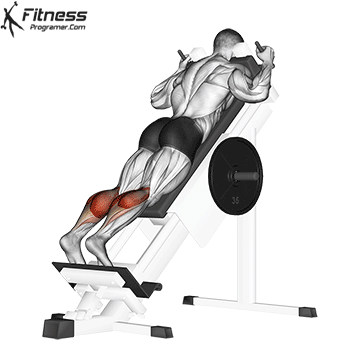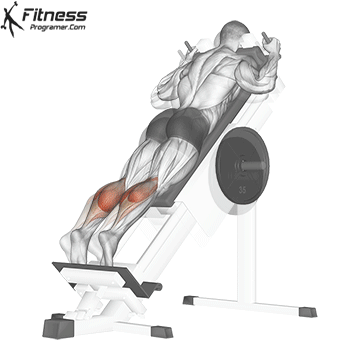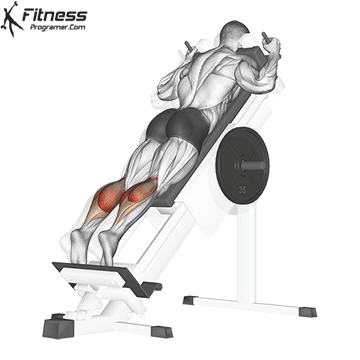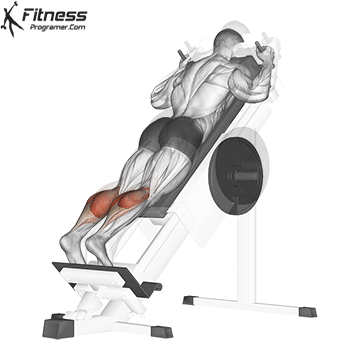
The alternatives are better to target calves directly
Squats direct calves to smaller, they Not ideal for calf hypertrophy or power. To target the calf muscles directly:
- The upright calf will rise (gasockeneis)
- A sitting calf rises (Emphasizes solus)
- The donkey is rising a calf (Stretching for gastrosnius
- Uploaded jump or pletetrial (For explosive calves
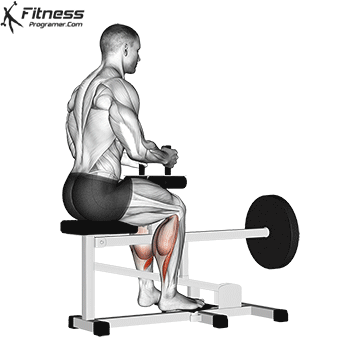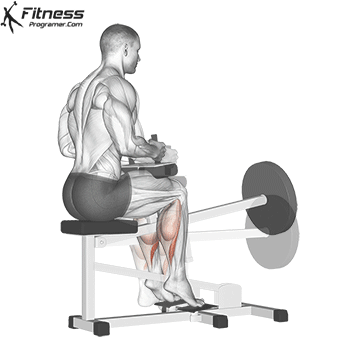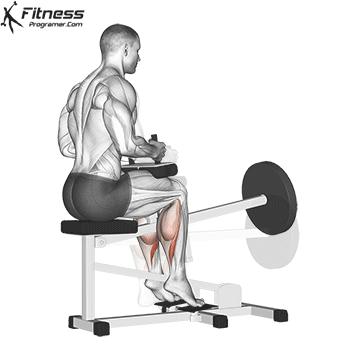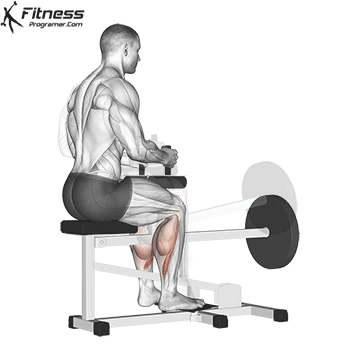
Summary: A sufficient belts for calves?
Not so much. Squats calf muscles but in the first place stabilityWithout inexperienced action. If you are seriously treating your calves, avoid aesthetics, performance or injury Calf preparation should be part of your program.
However, squares are an integral part of any comprehensive layer in the lower body, and the indirect connections of their calves provide ankle and knee joint integrity.
Literature
- COMPISSAN, A., Moss, Moses, RFs, Pelling, Tk, Wudrafu, K., Lewis, VC, KUMB, T. (2002). 4 The effect of the back bottom of emg activity of emg activity of the surface hips and thighs. Strengthening Air Conditioning Research16 (3), 428-432.
- Esskamillala, RF (2001). The laptural biomechanics of dynamic compression training. Medicine and fan for sports and exercise33 (1), 127-141.
- Schoenfeld, BJ (2010). Apply to mechanisms and resistance of muscle hypertrophy. Strengthening Air Conditioning Research24 (10), 285-2872.
- Konrad, P., & Shitts, K. (2008). EMG course of concrete joint stabilizers through Squats and other functional functions. Journal of Electronomicography and Cinorology18 (6), 907-917. Link to Absue