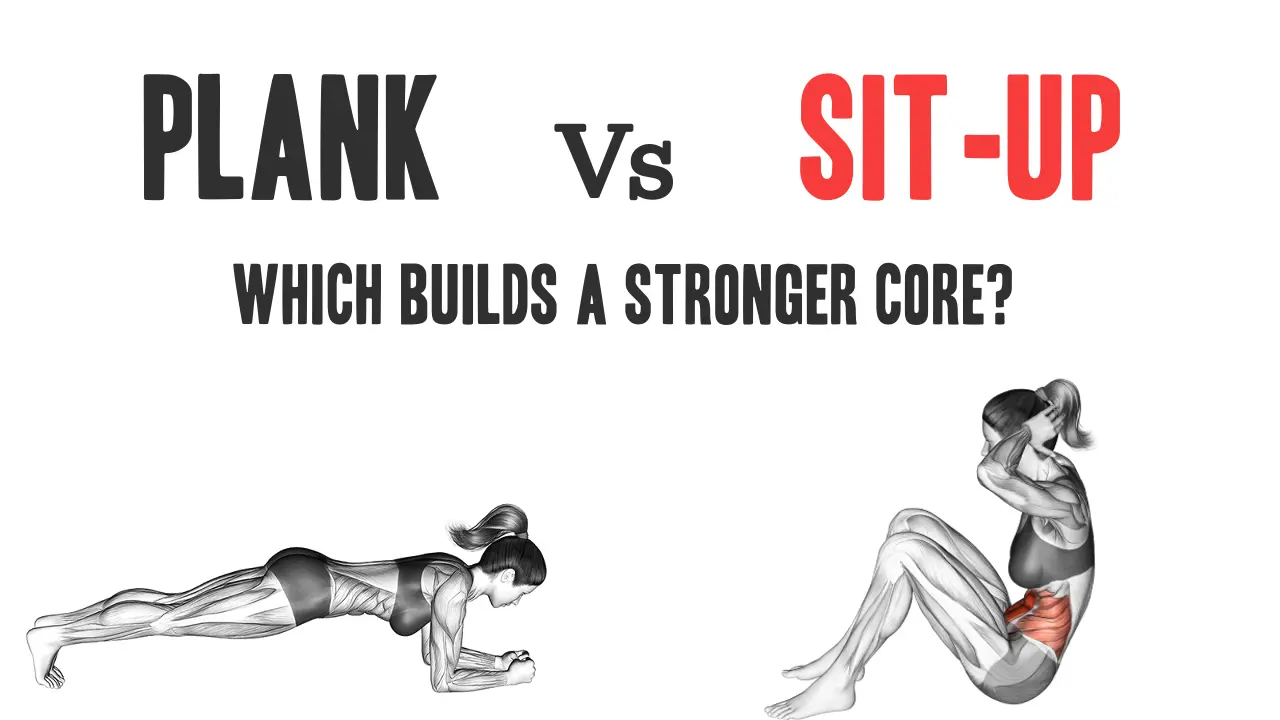
Stronger, more functional nucleusDo I have to be surprised by many elders and fitness fans often or pay more attention to where sitting? Although both exercises are known, they actually approach the main activities differently.
It board it Isometric exercise It emphasizes stability, postalability control and the resistance of the muscles.
On the other hand, sitting a Dynamic action This emphasizes the power of moving mobility and contraction through the backside of the abdominal cavity.
Each method has a set of own benefits and restrictions, depending on the quality of your activities, return and general action. Will be reviewed in this article the differences between boards and sitesFor example, solving themes Nuclear activation, the spinal health of, nuclear powerand Functional operationand to help you solve best which exercises.
Nuclear Anatomy: What Want to Strengthen?
Term “Core” It contains more than the visible abdominal muscles. The main components are:
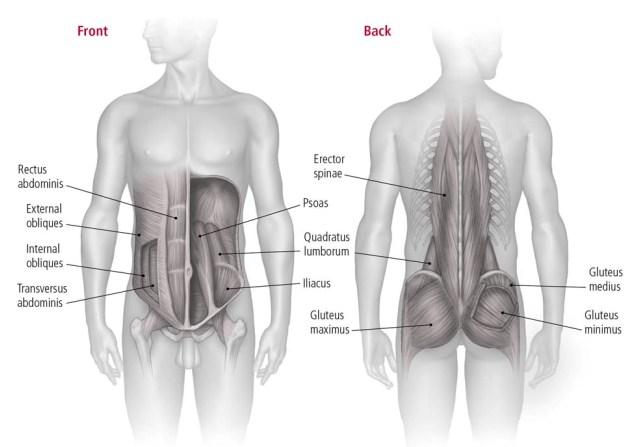
- In the rector of the abdomen – The main flex is widespread and widespread during sitting.
- The abdomen – A deep stabilizer that helps the abdomen pressure maintain pressure in the abdominal cavity.
- Inland and outer branches – Assisting the tasks of rotation, lateral flex and anti-rotation.
- The Vertebrae of Director of the Earth – stabilizes the spine.
- A multifedus, pelvis and diaphragm – Often, it is often ignored, these muscles are necessary for postural control and spinal cord stability.
An effective key training program must apply Movement and stability Functions across previous, back and lateral chains.
What is Plank?
A board The right isometric exercise you hold properly – when you support your weight on your wrists and toes. Your spine is a neutral positionAnd the muscles in front of your main nucleus are not moving without any joint movement.
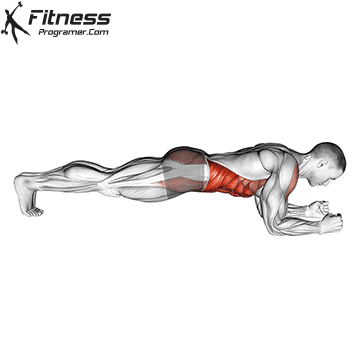
The main benefits of planks:
- Promotes spinal cord stability and reduces excess lumber movement.
- Trains the abdomen and deep nuclear muscles that are difficult to deal with dynamic exercises.
- The changes can be secured safely (e.g., side boards, rkc boards, loud ages).
- High offers Core endurance value by compressing less meters.
The planks are widely used for rehabilitation, sports and general fitness parameters injuries and multifaceted risks.
What is the passage?
It sitting Classic main trunk exercises, the internship starts with a position and raises the toron towards the knee. It is celebrated in the first place In the rector of the abdomen and to less level, Fections hips For example, such as Ilhihaas and Rectus Femoris.
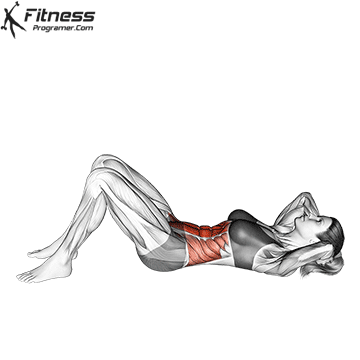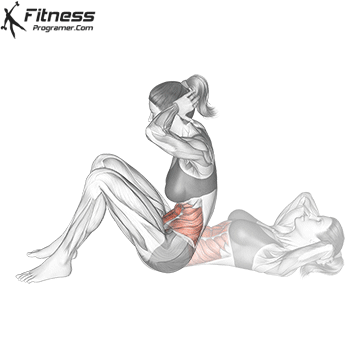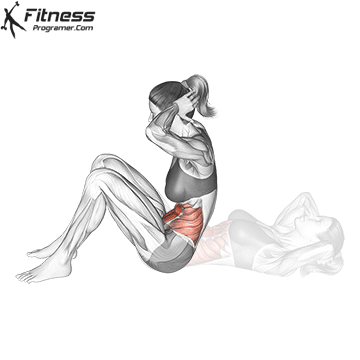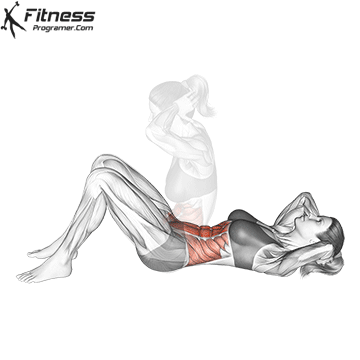
Advantages of passing:
- To build dynamic in the abdominal muscles.
- Gives encouragement Active UMUZTA Flactionimproves mobility when executed.
- Deals with Fections hips And other highlight flexums contribute to the Athletics movement.
However, the sites also include The load rearing several times raisedWhen the lumber was fulfilled incorrectly intensified.
Comparison to activate muscles
| Exercise | The primary muscles worked | Type of contraction |
|---|---|---|
| Board | Abdominal cavity, rectus abdomen, crooked, many lines | Isometry (static holder) |
| Sitting | Rectus abdomen, hips, rods | Dynamic (concentric / eccentric) |
Both exercises activate the core board Columns in development The power of static posts and deep collection, whereas sitting Focuses more attention Motor Rectus is in the abdominal cavity.
Risk of the feedback and injury
This is probably the most controversial aspect of the plank and turn-up.
- Boards a neutral spine and is usually considered regretEspecially for individuals who are pre-existing pain or disk.
- Places, especially in accelerating the leg, or performing with anchor can be multiplied Lomber Spine Stocks and Crossing Forces. The repetition increases the risk of releasing individual individuals (McGilil, 2007) disk, especially with the poor form.
Biomechanical Expert Dr. Stuart McGill, Bio Stuart McGill, planks prefer Development of nuclear stability without violating the spineSeating for some populations is contraindicated.
Core settings and Core Power: What is your goal?
- If your goal is to build durabilityStability and post control for activity for a long time, boards and their change is superior.
- If your target is developing strength and force Dynamic trunk behavior, especially for sports such as struggle, gymnastics or mm, Exercise based on site-up and flexibility can still play a roleA portable integrity is provided.
A well rounded program may include both, however boards are more sides and suggests of fewer risks In general in populations.
Programming Recommendations
For beginners or back pain:
- Start with Wrist PlanksHold for a long time, such as improving endurance.
- Add sideboard and bird dogs to the translation and to attract the back.
For athletes or progresses:
- Add Dynamic planks (For example, pull the shoulder, to enhance the difficulty.
- Use Managed site-up changesuch as Switzerland Ball Crunches or Dead mistakesslowly and with a firm shape.
Weekly Basic Plan Example:
| Day | Exercise | Set Duration / Reps |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Front board | 3 × 30-60 seconds |
| Wednesday | Sideboard (each side) | 3 × 30 seconds |
| Friday | A dead error or controlled sitting | 3 × 10-12 slow, managed representatives |
Conclusion: Will he build a strong nucleus?
Both boards and sittings Offer useful, but they serve for different purposes. For most people, especially for people who resist the Otomenal Health, Poster resistance or functional movement, boards are the highest choice. They are sustainable stability, reduces the risk of injury and supports sports indicators in various sports and events.
The site-upts may still be useful to intensify the Rectus abdominal cavity, but they should be careful, especially if Lomber is concerned. The end is the best Basic curricula integrate Isometric and dynamic elementsBalance of mobility for balance and building a good trunk.
Literature
- McGill, cm (2007). Low discounts: Prevention and rehabilitation of evidence. Human beer.
- EXPOM, RA, DONATELY, RA, & CARP, KC (2007). 9 In the rehabilitation exercise, the main trunk, the hip, the hips, the electromitrogy analysis of the number muscles. Jasop sports sports37 (12), 754-762.
- Ahtler, CT, & McGill, cm (1997). Low rear cargo on different exercises in the abdomen: search for the safest suffering of the abdomen. Medicine and fan for sports and exercise29 (6), 804-811.
- Worshardson, JM (2007). Sustainability Training: Applications for sports air conditioning programs. Strengthening Air Conditioning Research21 (3), 979-985.
- Schoenfeld, BJ (2010). Apply to mechanisms and resistance of muscle hypertrophy. Strengthening Air Conditioning Research24 (10), 285-2872.