High-level performance in sports and fitness is never based on one physical quality. Instead, this is The interdependence of work-related fitness componentsUnique Power, strength, speed, agility, flexibilityand durability– This creates the edge of the athlete.
As mentioned Component and Carrer’s sports air conditioning model and supported Scientific research reviewed by equalOptimization of one component often increases several. In this article, these components will provide specialists to how to teach them effectively and raise them.
What are the components of fitness related fitness related fitness?
This is physical features Sporting. Unlike health-related components (e.g., body composition, main cardiovascular health), Performance features is responsible for:
- Explosive action
- A steady tension exit
- Quick direction changes
- The ability to work long lasting
They should not be separated from each other.
1. Power: Fundamentals of all physical qualities
Description: The ability to create force against opposition (Power × distance).
Why is this important: The power is a foundation that develops force, speedand Prevent haste.
“A force is a match that will lead to all other adaptations.” Charles Staley
Types of training:
- Isometry (static): Plancs, gymnasts
- Dynamic: Squats, Deadlifts, bench press
- Power-dominant: Olympic elevators
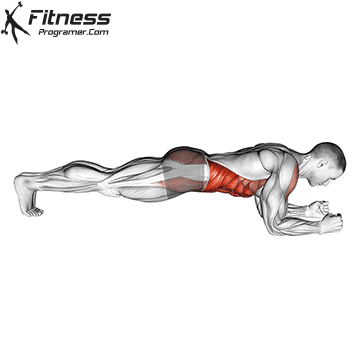
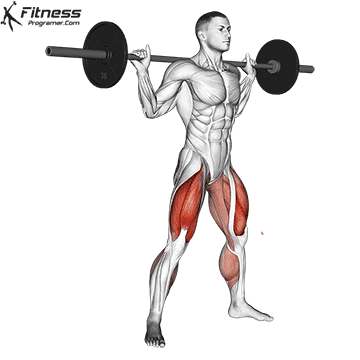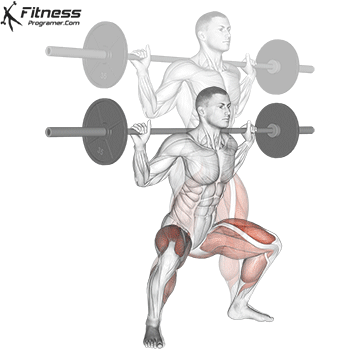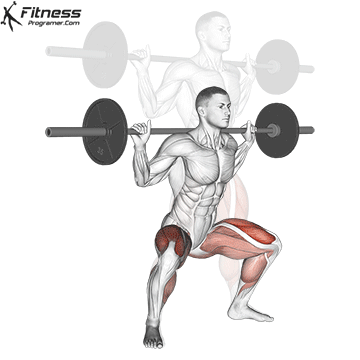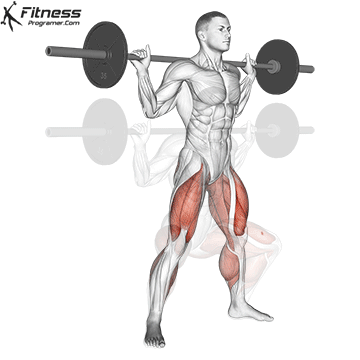
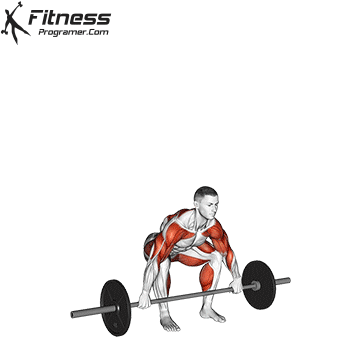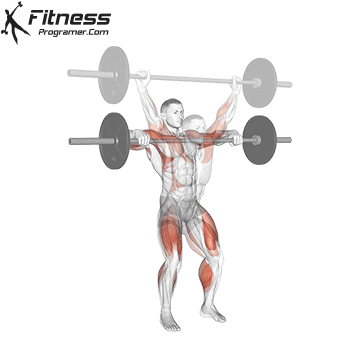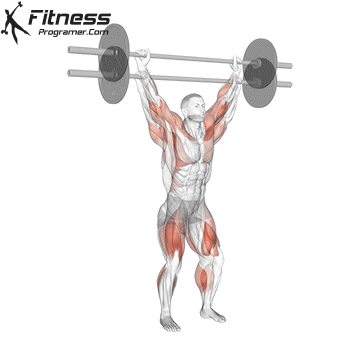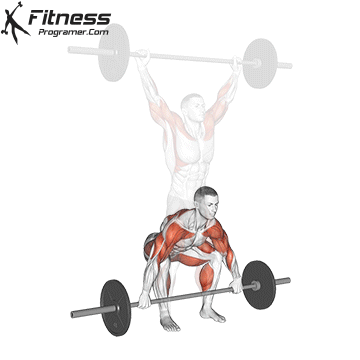
Evidence: Trained In young athletes reduce the risk of injury (Figurebaum & Shram, 2004).
2. Power: Power and speed bridge
Description: Power = Power × Delivery ÷ Time
Main character: Combination force with Performance speed.
Applications:
- Olympic elevators
- Sparing
- Jump
- Shooting
The concept of research: Force more dependent Development Only from moving speed (“BIRDAN 2015”).
3. Speed: Maximum speed speed
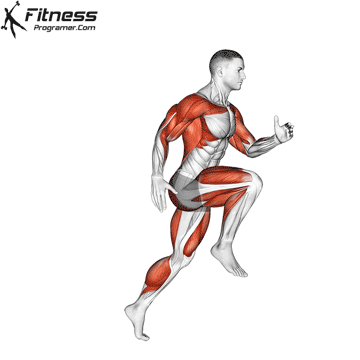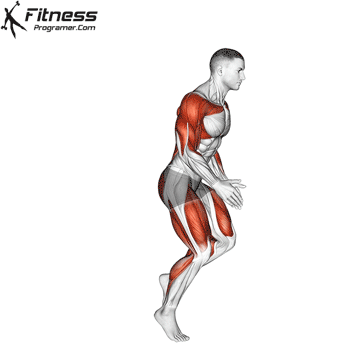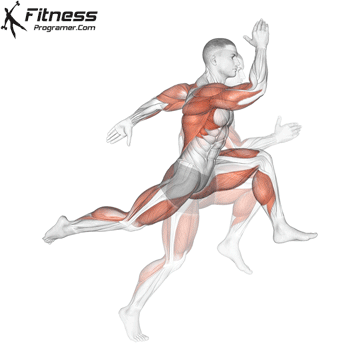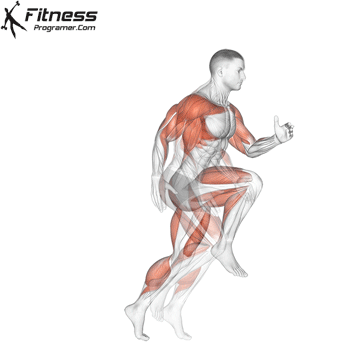
Description: Speed = Distance ÷ Time
Interior minorities:
- Reaction time (to respond to stimulus)
- Movement time (ending the action)
- Sprint speed (stridee length × travel frequency)
Dependence on training: Strong, strong muscles increase the highest speed.
Note: Speed weakly limited and provided with coordination.
4. Reacness: Quicks in a fast, managed direction
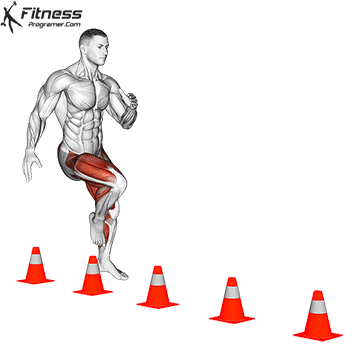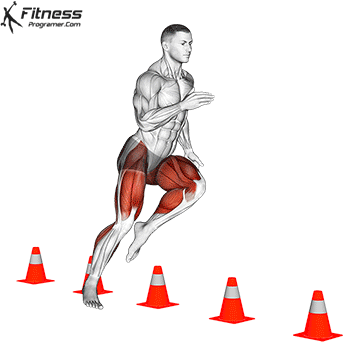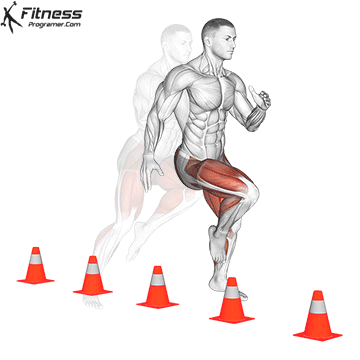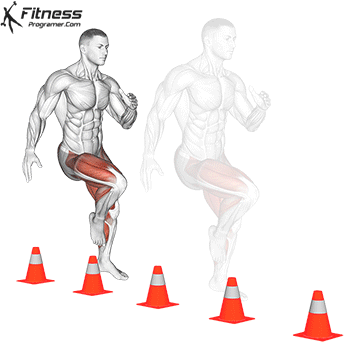
Description: The ability to make and modify direction more effective.
Relyes on:
- Strength and force For a strong slowing / recycling
- Car control For coordination and body awareness
Curriculum: Do not repeat the same drill repeat. Agenside must be A variation of sports to prevent plateau.
5. Durability: Sustainable production over time
Aerobic durability
- Long, sedimentary effort (> 3 minutes)
- Example: Running in distance, long collections
Anaerob durability
- Short, strong explosions (<60 seconds)
- For example: Sprint, Interval Service
Types of muscles:
| Species | Instance |
|---|---|
| Uninterrupted | Boards, rise |
| Isometric | Static protection, isometric |
| Dynamic | Oars, high repensation |
| Short rest / high strength | Regional training, football |
These species are available in a permanent And it is often repeated according to the demands of sports.
6. Flexibility: The operating range of the action
Dynamic flexibility:
- Performed before training
- Power increases joint mobility without loss
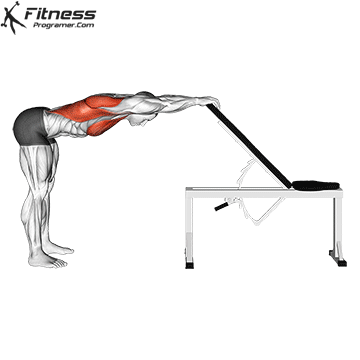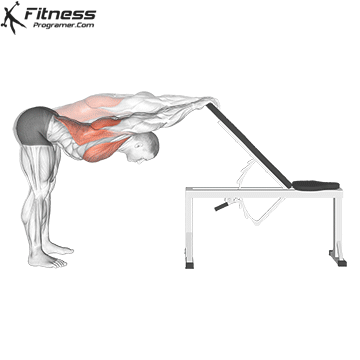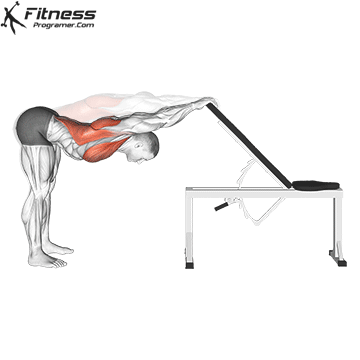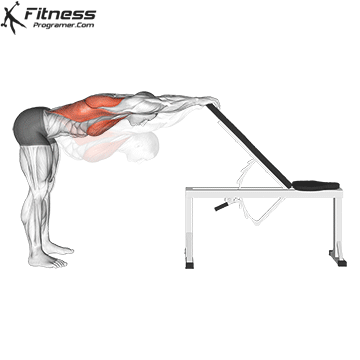
Static flexibility:
- The best of training is best
- Used for places used with hardness (Based on screening)



Scientific warning:
A static extent before the mash-exercise can Reduce power and strength By an hour (Evetovich, and others, 2003 and 2003).
Context-specific use:
- Gymnasts and fighters require high frame
- Excessive flexibility can prevent the type of electricity energy (Jones, 2002)
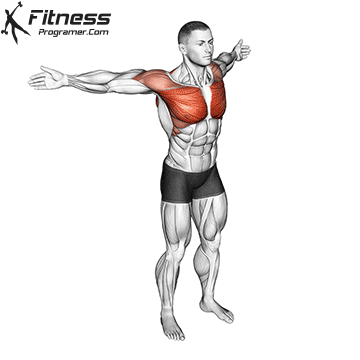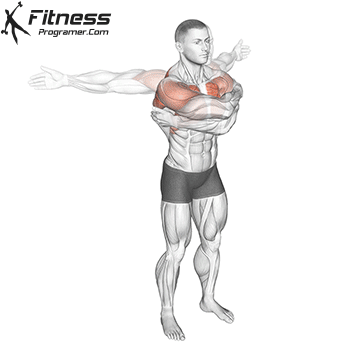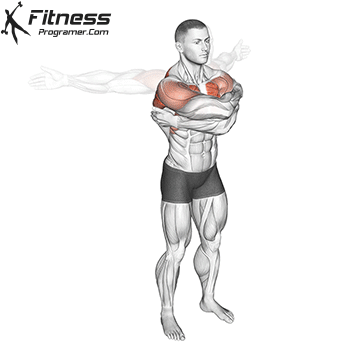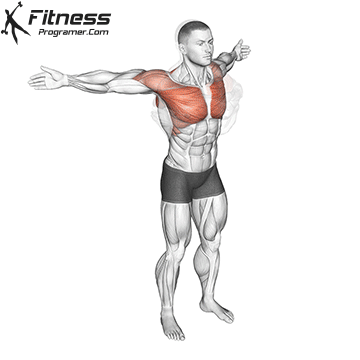
7. Coordination and Development of Motor

Coordination includes:
- Time
- Rhythm
- Spatial awareness
- A sequence of action
Coordination is raw materials binds raw materials. All athletes benefit from the stock exchanges of neesecaturz and control of control.
Educational principles you need to know
1. The uniqueness: A trains in a sport or purpose.
2. Excessive shipping: Gradually increase intensity or size.
3. Change: Circle the stimulus to prevent plateau.
4. Restore: Respect the remaining educational effects – every quality of each fitness is broken in a different rate.
| Adaptation | How long does it last (average) |
|---|---|
| Force | 30+ days |
| Durability | 15-30 days |
| Speed | 5-10 days |
Summary: Why do it all works together
Fitness components associated with operation will not work in silage. How is your ability to splint, jump, change the direction or recover from fatigue Your whole physical system works together.
You apply for a coach, athlete or recreational station Power, power, speed, endurance, adaptability and coordination Solidarity is a way of work in progressive.
Literature
- Company T, Carrera M. (2015). The state of the young athletes. Human beer.
- Figigentbaum AD, SHRANB J. (2004). Can you reduce injuries in youth sports? Power and Air Conditioner Log26 (3): 16-21.
- Evetovich Tk and others. (2003). Static stretching effect on the moment. J toop Canf17 (3): 484-488.
- Young WB, Mehb Dg. (2003). Stretching and explosive work. J Sport Medf Fitness43 (1): 21-27.
- JONS AM. (2002). Working flexibility Str j sports Med23 (1): 40-43.




